The integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and robotics into manufacturing industries is reshaping how products are designed, produced, and delivered. These technologies are driving the fourth industrial revolution by enhancing operational efficiency, improving precision, and fostering innovation. This article explores the transformative impact of AI and robotics on manufacturing industries, highlighting their applications, benefits, and challenges.
Key Applications of AI and Robotics in Manufacturing
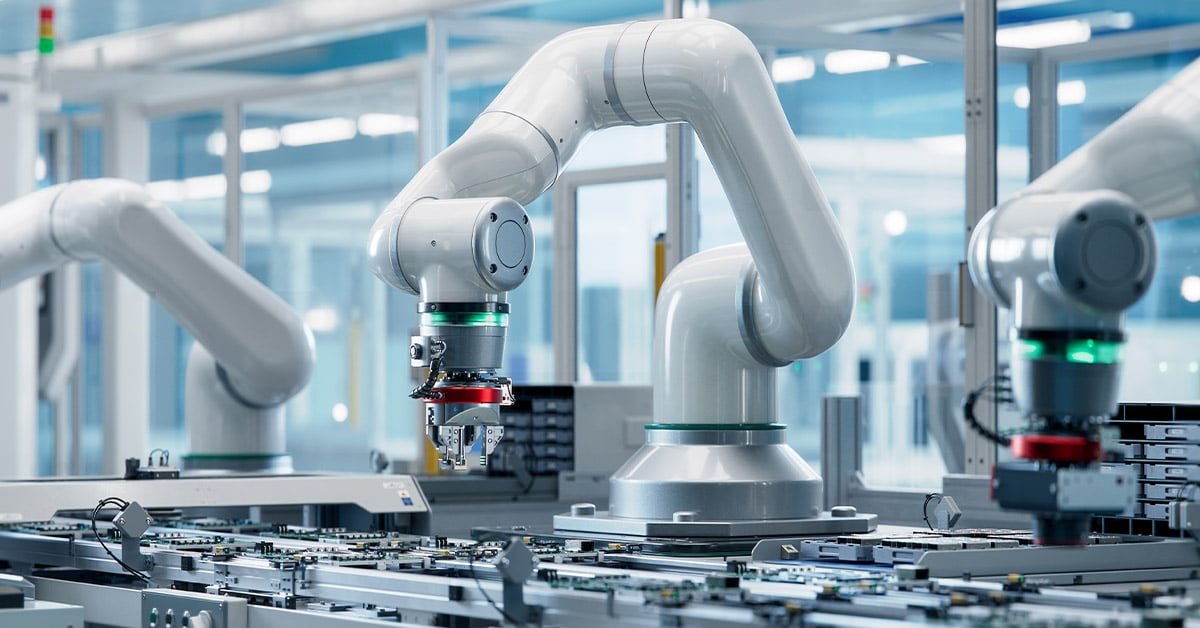
1. Automated Production Lines
AI-powered robots are revolutionizing production lines by automating repetitive and labor-intensive tasks. These robots can perform complex operations with high precision, leading to increased production speeds and reduced error rates.
Applications:
- Assembly: Robots handle assembly tasks, from simple parts to intricate components.
- Packaging: Automated systems manage packaging, labeling, and quality control.
Benefits:
- Increased Efficiency: Boosts production rates and minimizes downtime.
- Consistency: Ensures uniform quality and reduces human error.
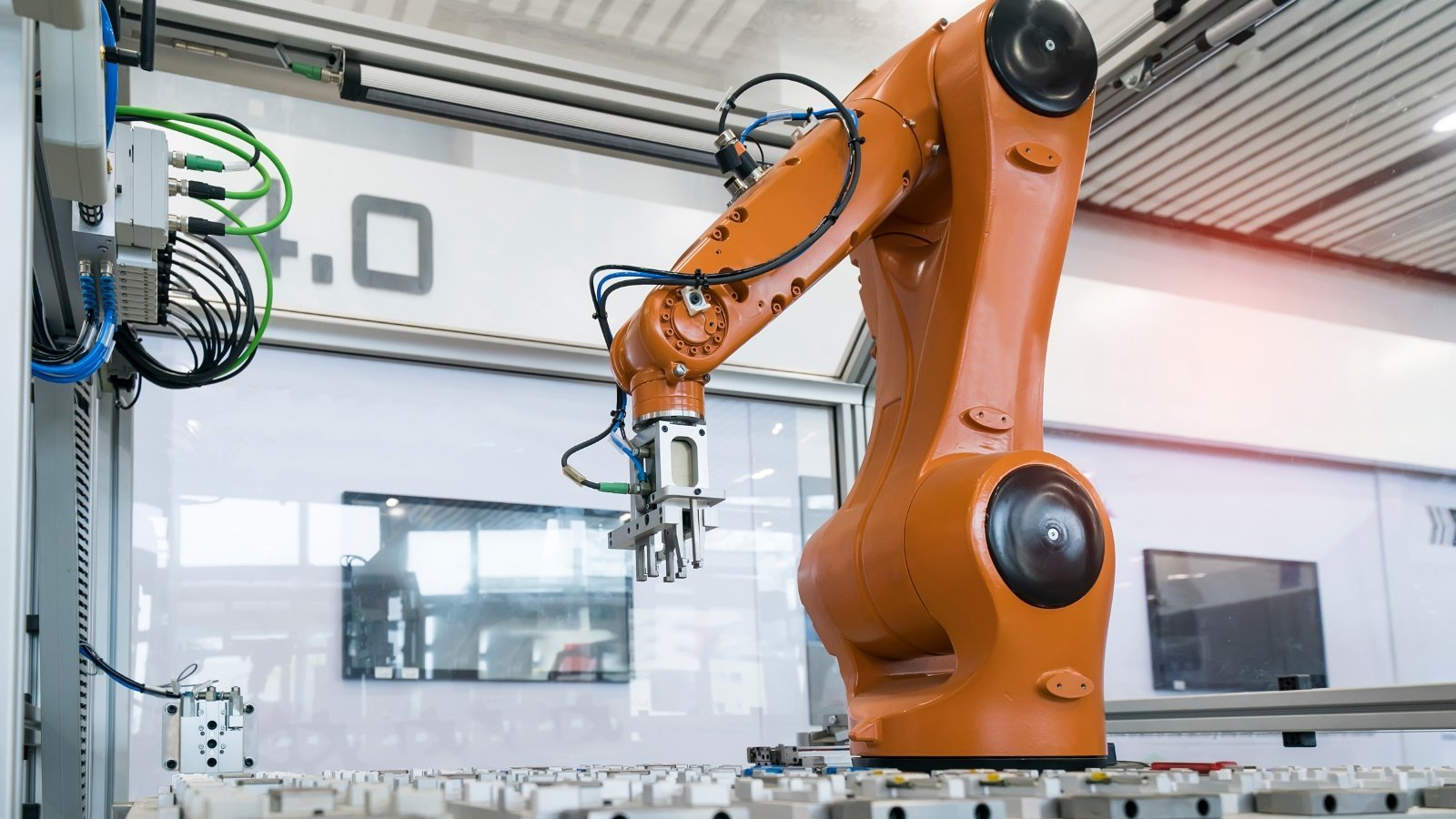

Challenges:
- High Initial Costs: Significant investment in robotic systems and infrastructure.
- Maintenance: Ongoing maintenance and calibration are required to ensure optimal performance.
2. Predictive Maintenance
AI technologies enable predictive maintenance by analyzing data from machinery and equipment. Machine learning algorithms identify patterns and predict potential failures before they occur, allowing for timely maintenance and minimizing production disruptions.
Applications:
- Monitoring: Continuous monitoring of equipment health and performance.
- Analysis: Data-driven insights into potential issues and maintenance needs.
Benefits:
- Reduced Downtime: Prevents unexpected equipment failures and production halts.
- Cost Savings: Reduces repair costs and extends equipment lifespan.
Challenges:
- Data Management: Requires robust data collection and analysis systems.
- Skill Requirements: Needs skilled personnel to interpret data and implement maintenance strategies.
3. Quality Control and Inspection
AI-driven vision systems and robotics are enhancing quality control processes by inspecting products for defects and inconsistencies. These systems use machine learning and computer vision to detect issues with high accuracy.
Applications:
- Defect Detection: Identifying defects in real-time during the production process.
- Inspection: Verifying product dimensions, finishes, and assembly quality.
Benefits:
- Enhanced Accuracy: Provides precise and consistent quality inspections.
- Efficiency: Speeds up the quality control process and reduces manual inspection efforts.
Challenges:
- Calibration: Requires regular calibration and fine-tuning to maintain accuracy.
- Integration: Integrating vision systems with existing production processes can be complex.
4. Flexible Manufacturing Systems
AI and robotics enable flexible manufacturing systems that adapt to changing production requirements and product designs. These systems can quickly reconfigure production lines and adjust to new tasks, enhancing manufacturing agility.
Applications:
- Customization: Adapting production lines for custom or small-batch manufacturing.
- Reconfiguration: Easily reconfiguring robots and systems for different products.
Benefits:
- Adaptability: Responds to market demands and changes in product design.
- Resource Optimization: Maximizes the use of manufacturing resources and reduces waste.
Challenges:
- Complexity: Designing flexible systems requires advanced planning and integration.
- Training: Operators need to be trained to manage and adjust flexible manufacturing systems.
Benefits of AI and Robotics in Manufacturing
- Increased Productivity: Automation and AI enhance production rates and efficiency.
- Improved Precision: Robotics and AI systems provide high accuracy and consistency in manufacturing processes.
- Enhanced Safety: Reduces the need for human operators to perform dangerous tasks, improving workplace safety.
- Cost Reduction: Automation lowers labor costs and reduces waste, leading to cost savings.
Challenges and Considerations
- Initial Investment: High upfront costs for purchasing and integrating AI and robotic systems.
- Skill Requirements: Need for skilled personnel to operate, program, and maintain advanced systems.
- Integration: Challenges in integrating new technologies with existing systems and processes.
- Data Security: Ensuring the security of data generated and processed by AI and robotics systems.
The Future of AI and Robotics in Manufacturing
The future of AI and robotics in manufacturing holds exciting possibilities:
- Advanced AI Algorithms: Continued advancements in AI will lead to more sophisticated and capable systems.
- Collaborative Robots (Cobots): Growth in collaborative robots that work alongside human operators in a shared workspace.
- Smart Factories: Development of fully automated and interconnected smart factories that optimize production processes in real-time.
- Sustainable Manufacturing: AI and robotics will contribute to more sustainable manufacturing practices by reducing waste and energy consumption.
Conclusion
AI and robotics are transforming manufacturing industries by driving efficiency, precision, and innovation. From automated production lines and predictive maintenance to quality control and flexible manufacturing systems, these technologies are reshaping how products are made and delivered.
While challenges such as high initial costs and integration complexities exist, the benefits of AI and robotics in manufacturing are substantial. Embracing these technologies will enable manufacturers to stay competitive, adapt to evolving market demands, and achieve greater operational excellence.
As AI and robotics continue to advance, their role in manufacturing will become even more integral, offering new opportunities for growth, efficiency, and innovation in the industry.
4o mini