Choosing between cloud-based and on-premises software is a crucial decision for businesses. Both options offer unique benefits and challenges. Understanding the differences between them can help you make an informed choice that aligns with your organization’s needs. This article compares cloud-based and on-premises software across several key factors.
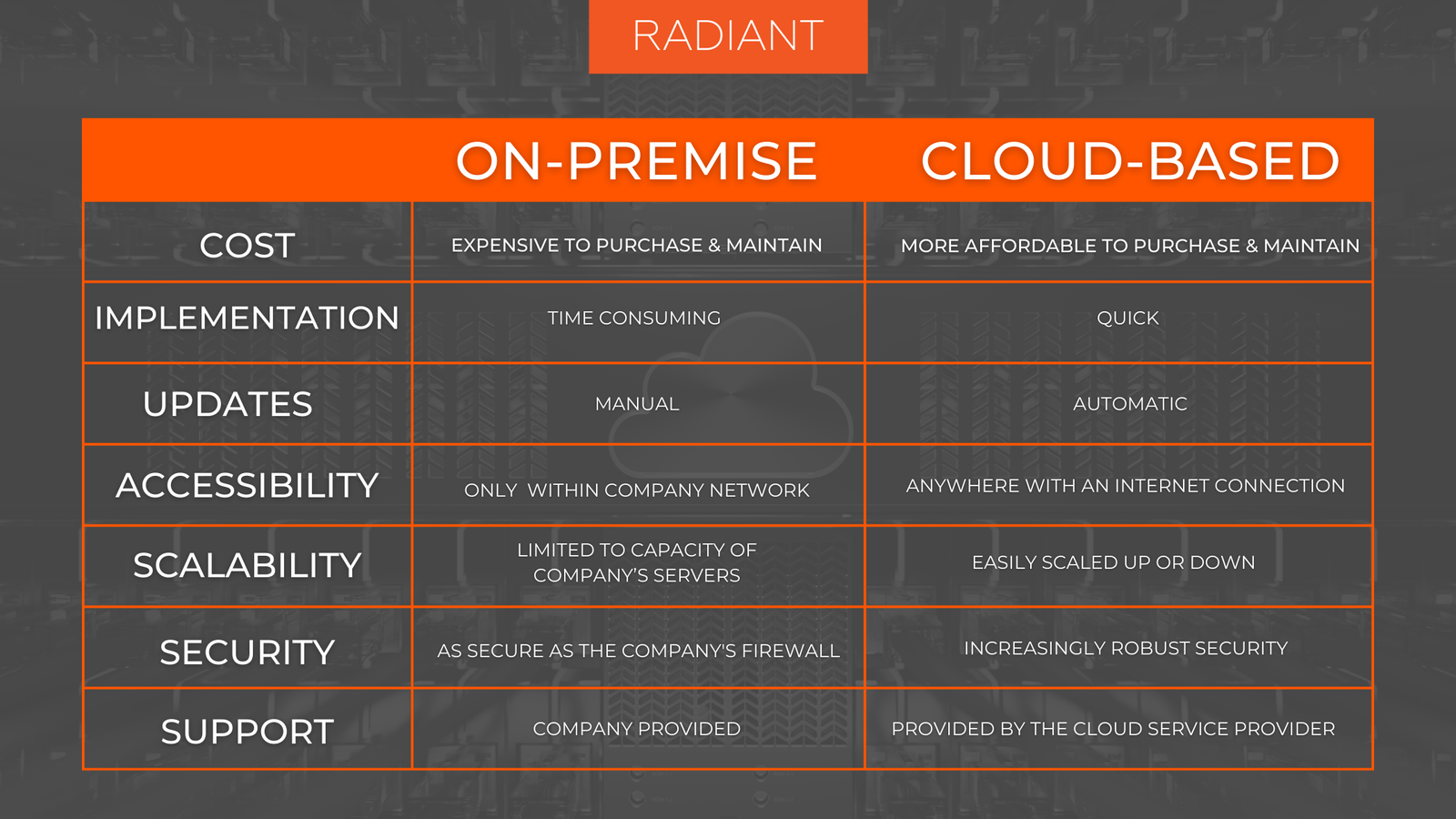
Cost Considerations
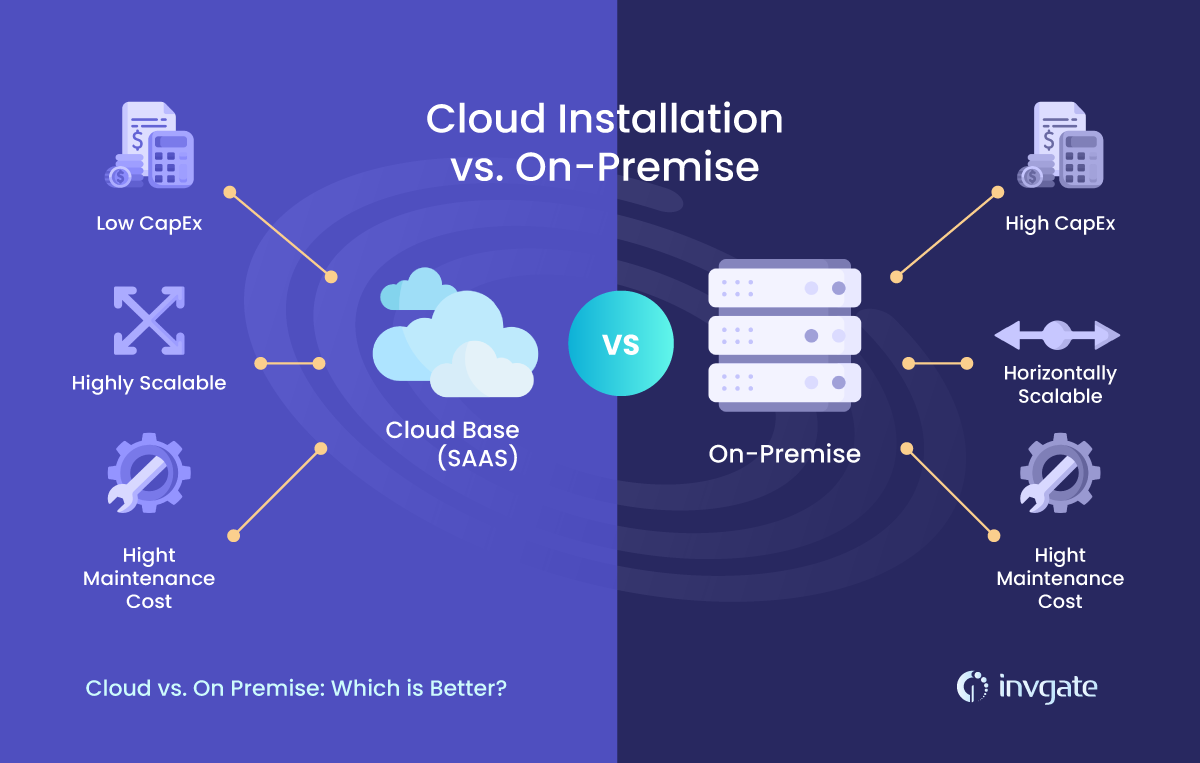
Cloud-Based Software: Cloud-based software typically operates on a subscription model, with costs based on usage or number of users. This model eliminates the need for large upfront investments in hardware and infrastructure. Businesses pay for what they use, which can be more cost-effective, especially for small to medium-sized enterprises.
On-Premises Software: On-premises software requires a significant upfront investment in hardware and licenses. Additionally, there are ongoing costs for maintenance, upgrades, and IT staff. While the initial cost can be high, some organizations may find it more economical in the long run if they have the infrastructure and resources to manage it.
Scalability and Flexibility
Cloud-Based Software: Scalability is a key advantage of cloud-based software. It allows businesses to adjust resources based on demand, scaling up or down easily as needed. This flexibility supports growth and adaptation without requiring significant changes to infrastructure.
On-Premises Software: Scaling on-premises software can be challenging and costly. It often involves purchasing additional hardware and software licenses, which can be time-consuming and expensive. As a result, businesses may face limitations in scaling their operations quickly.
Security and Compliance
Cloud-Based Software: Cloud providers invest heavily in security measures, including data encryption, firewalls, and intrusion detection systems. They also ensure compliance with industry standards and regulations. However, businesses must trust the provider’s security practices and may have less control over data management.
On-Premises Software: On-premises software offers more control over security and compliance, as organizations manage their own infrastructure and data. This can be advantageous for businesses with stringent security requirements or regulatory obligations. However, maintaining security requires dedicated resources and expertise.
Maintenance and Updates
Cloud-Based Software: Cloud-based software is maintained and updated by the provider. This ensures that users have access to the latest features and security patches without needing to perform manual updates. It reduces the burden on internal IT staff and ensures that the software remains current.
On-Premises Software: On-premises software requires manual updates and maintenance by internal IT staff. This can be time-consuming and may involve downtime for upgrades. Businesses are responsible for ensuring that their software is up-to-date and secure, which can be resource-intensive.
Accessibility and Remote Work
Cloud-Based Software: Cloud-based software provides remote access from any location with an internet connection. This is ideal for supporting remote and hybrid work environments, allowing employees to collaborate and access resources from anywhere.
On-Premises Software: On-premises software is typically accessed through a local network, which can limit remote access. While remote access solutions are available, they often require additional configuration and may not be as seamless as cloud-based options.
Backup and Disaster Recovery
Cloud-Based Software: Cloud providers usually include backup and disaster recovery options as part of their services. Data is often stored in multiple locations, providing redundancy and minimizing the risk of data loss. This built-in protection helps ensure business continuity.
On-Premises Software: Backup and disaster recovery for on-premises software are the responsibility of the organization. Businesses must invest in backup systems and recovery plans to protect their data. This can be complex and costly, requiring dedicated resources and planning.
Customization and Integration
Cloud-Based Software: Cloud-based software often offers a range of customization options, but there may be limitations compared to on-premises solutions. Integration with other cloud-based tools is typically straightforward, enhancing overall functionality.
On-Premises Software: On-premises software can be highly customized to meet specific business needs. It may also offer more flexibility for integration with existing systems. However, customization and integration can be complex and require significant development effort.
Conclusion
Choosing between cloud-based and on-premises software involves evaluating factors such as cost, scalability, security, and maintenance. Cloud-based solutions offer flexibility, cost-effectiveness, and remote accessibility, while on-premises software provides more control and customization options. By considering these factors, businesses can make an informed decision that aligns with their operational requirements and strategic goals.